
Under 100 Words: A Compact Summary
In February, US consumer prices showed a significant increase, with the annual inflation rate rising to 3.2%. The Federal Reserve responded by aggressively raising interest rates. Despite concerns, Fed Chair Powell hinted at policy easing later in the year, prompting speculation about a rate cut in June (Surprise Spike in US Inflation).
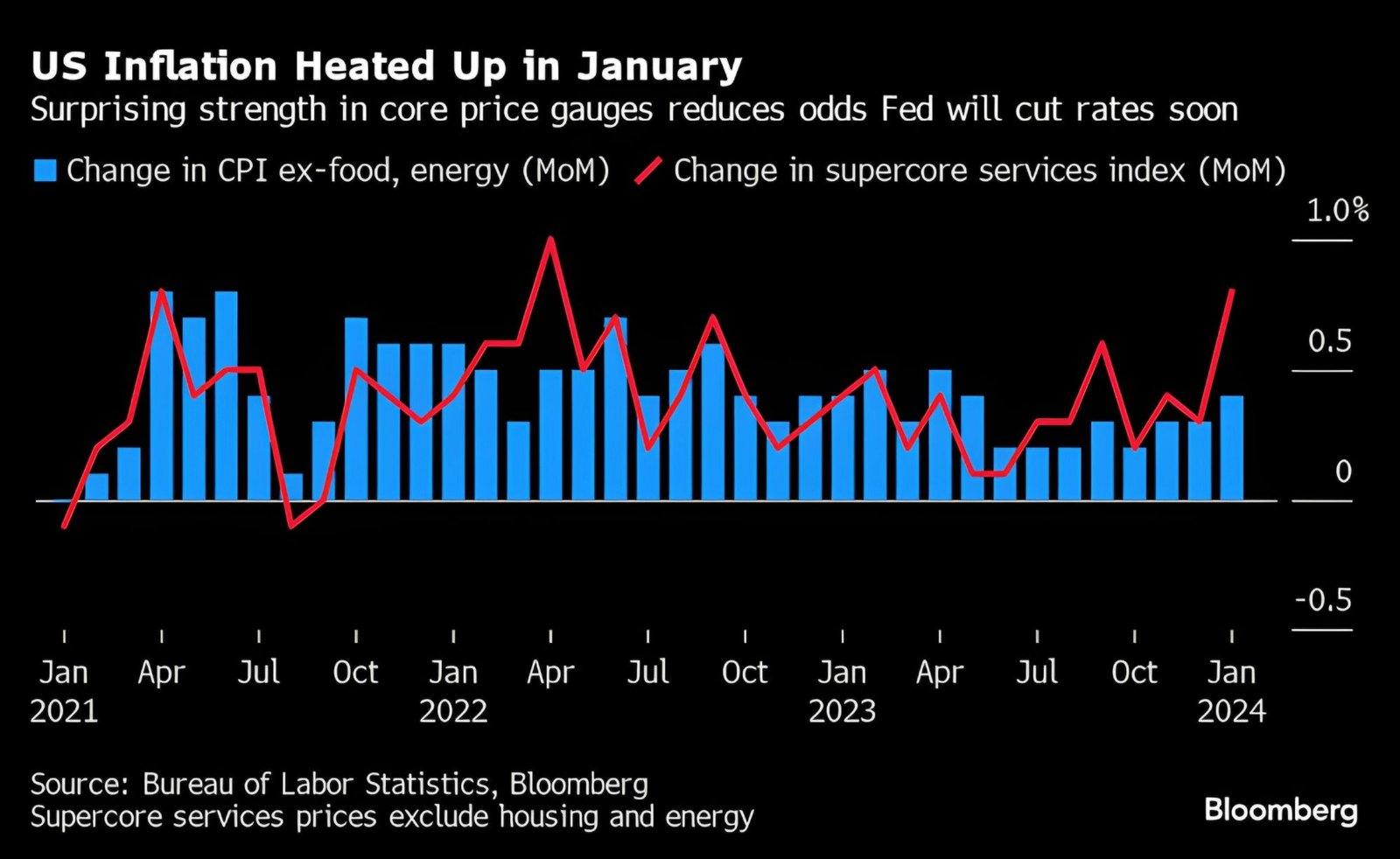
- In February, inflation figures released by the Labor Department revealed a notable increase in both monthly and annual US consumer prices.
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a frequently monitored inflation indicator, saw a 3.2 percent annual increase in February, with a 0.4 percent rise in the last month alone (Surprise Spike in US Inflation). The annual inflation rate has edged up slightly from 3.1 percent in January.
- This marks a shift from the previous downward trend, as the current inflation rate surpasses January’s 3.1 percent but remains below the 3.4 percent reported in December. However, the Federal Reserve (Fed) still needs to strive for its 2 percent target rate.
- To counteract excessive inflation, the Federal Reserve (Fed) has implemented robust policy measures, aggressively increasing interest rates to mitigate demand and stabilize prices (Surprise Spike in US Inflation).
- Starting from March 2022, the Fed has incrementally raised interest rates through periodic adjustments, aligning the standard federal fund rate within the targeted range of 5 to 5.25 percent (Surprise Spike in US Inflation).
- Investors are likely to closely scrutinize the fluctuations in both stock and cryptocurrency markets in reaction to the CPI data.
- The increase in inflation aligns with a notable upswing in the cryptocurrency market, especially after the introduction of a Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) in the United States.
- According to Reuters, the US Federal Reserve is expected to reduce its benchmark interest rate in June, as the central bank awaits additional data to determine whether inflation is progressing toward its 2% target (Surprise Spike in US Inflation).
- In the latest survey conducted by Reuters, respondents indicated that there was a higher likelihood of a reduction in the median view of rate estimates if Federal Reserve policymakers make changes during the upcoming March 19-20 meeting.
- In his recent statement to Congress, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell underscored the appropriateness of policy easing at some point this year. He emphasized that persistent inflation and a robust labor market might impede an early rate decrease (Surprise Spike in US Inflation).
- A poll conducted between March 5 and 11 with 108 participating economists revealed that all projected the fed funds rate to remain in the 5.25%-5.50% range next week. Of these, 72 anticipated the first rate decrease in June, 17 predicted cuts in May, and 19 others foresaw reductions in July or later.
- Michael Gapen, Chief US Economist at Bank of America, commented to Reuters, stating, “The Fed is seeking ‘greater confidence’ on inflation before it starts normalizing its policy stance. We expect progress on inflation in the coming months will give the Fed enough confidence to begin a gradual cutting cycle in June.”
ALSO READ – The Body Shop Exits US Market, Canadian Stores to Close Amid Bankruptcy.